Moo Deng - Hippo pathway x Cancer - [NO CANCER]
What is Hippo Pathway
The Hippo signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved network that plays a critical role in regulating various biological processes, including
- Regulation of Cell Growth and Proliferation - The Hippo pathway inhibits excessive cell growth and division by phosphorylating and inactivating YAP and TAZ
- Control of Organ Size - It ensures that organs grow to their appropriate size by balancing cell growth with cell death.
- Tissue Regeneration and Wound Healing
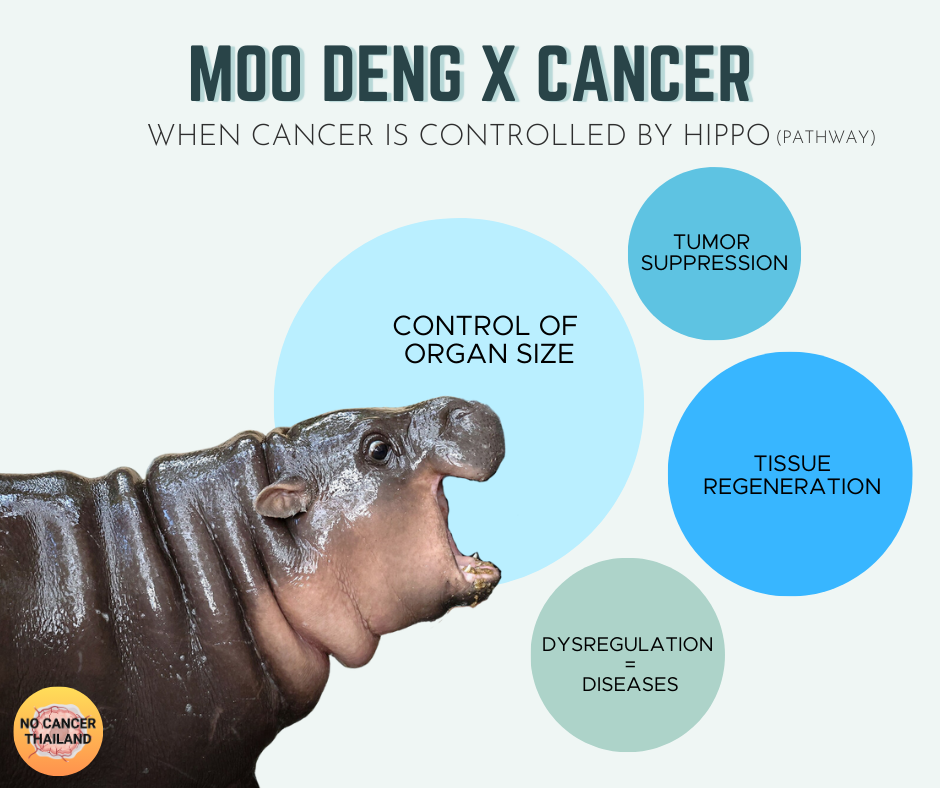
Moo Deng (Hippo pathway) controls human health and diseases, Photo by No Cancer THAILAND
Dysregulation and Disease Implications
Dysregulation of the Hippo pathway can lead to various diseases
😱 Cancer
💔 Cardiac Diseases
🫁 Pulmonary Diseases
🧪 Renal Diseases
🍸 Hepatic Diseases
👁️ Eye Diseases
🛡️ Immune Dysfunction
Key Roles of the Hippo Pathway in Cancer
- Tumor Suppression - The Hippo pathway acts as a critical tumor suppressor by inhibiting excessive cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to the uncontrolled growth characteristic of cancer.
- Oncogenic Activation - In many cancers, the Hippo pathway is found to be inactivated, resulting in the overactivation of YAP/TAZ. This promotes oncogenesis by driving the expression of genes that facilitate cell growth and survival, contributing to tumor progression
- Cancer Stem Cell Biology
🔬💊 Given its significant role in health and disease, targeting the components of the Hippo pathway has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy for treating various conditions, particularly cancers
🌟 Reference:
Fu, M., Hu, Y., Lan, T. et al. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther 7, 376 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01191-9